LED Cube/Column Resistors in Detail: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Marvin (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→uC) |
Marvin (Diskussion | Beiträge) (→LED) |
||
| Zeile 17: | Zeile 17: | ||
===LED=== | ===LED=== | ||
Dropout voltages for LEDs are somewhat more complex. Ranges can be found at [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-emitting_diode#Colors_and_materials Wikipedia] | |||
===Transistor Array=== | ===Transistor Array=== | ||
===Resistor=== | ===Resistor=== | ||
Version vom 15. April 2012, 02:28 Uhr
Choosing the right column resistors for your LED cube requires you to consider several factors:
- Suitability of the cube base for different colors
- Expected USB voltage
- Voltage drop on the microcontroller
- Voltage drop on the transistor array
- Voltage drop on the LED
For now, we are only interested in the resistor value for one specific LED color (and also only one type as a color may be created using different techniques which results in different forward voltages), thus only one LED forward voltage has to be taken into consideration. Also we assume that the USB voltage is 5.0 Volts which is okay, as we will see. Now we are at a situation where we have five volts which will be divided onto our components. Also, we are going to make this calculation only for 20 mA current per LED, however, you can make your own calculations quite easily. Let's have a look at the different I/V characteristics:
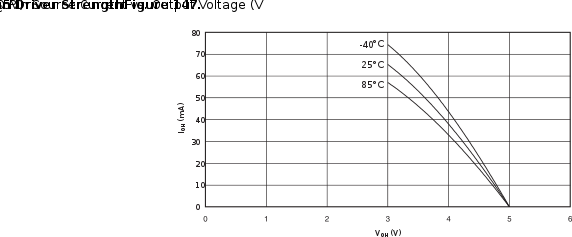
uC
This is a snippet from the ATmega8/L datasheet:
You can clearly see the dropout voltage. In our example with 20 mA current, we have a dropout of 0.5 V.
LED
Dropout voltages for LEDs are somewhat more complex. Ranges can be found at Wikipedia