LED Cube/PCB Lötanleitung: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| Zeile 20: | Zeile 20: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==USB | ==USB Zenerdioden== | ||
[[File:Zener.jpeg|thumb]] | [[File:Zener.jpeg|thumb]] | ||
Nun benötigen wir zwei 3.6 V Zenerdioden für die Datenleitungen, Z1 und Z2. Hier muss auf die Orientierung geachtet werden. Die (schwarze) Linie auf den Dioden gehört auf die Seite der einzelnen Linie auf dem Diodensymbol (gegenüber des Dreiecks) das auf das PCB gedruckt ist. Dies ist auf dem Bild auf der linken Seite zu sehen. | Nun benötigen wir zwei 3.6 V Zenerdioden für die Datenleitungen, Z1 und Z2. Hier muss auf die Orientierung geachtet werden. Die (schwarze) Linie auf den Dioden gehört auf die Seite der einzelnen Linie auf dem Diodensymbol (gegenüber des Dreiecks) das auf das PCB gedruckt ist. Dies ist auf dem Bild auf der linken Seite zu sehen. | ||
Version vom 20. April 2012, 09:41 Uhr
under construction
Vorlage:LED Cube Series Auf dieser Seite ist die Lötanleitung für den PCB des LED Cubes zu finden.
Ein vollständiges Schaltbild des PCBs kann hier runtergeladen werden: Datei:Cube.pdf.
USB Resistors
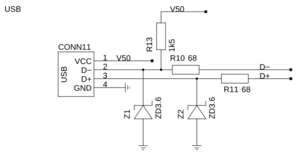
Als erstes verlöten wir R10, R11 und R13. Wie bei allen Wiederständen, die wir in diesem Projekt verwenden, ist die Ausrichtung nicht relevant. Die Wiederstandswerte und Farbcodes können in dem Schaltplan, oder der folgenden Tabelle nachgeschlagen werden:
| Name | Value | Color Code |
|---|---|---|
| R10 | 68 Ohm |  (blau-grün-schwarz-gold-braun) (blau-grün-schwarz-gold-braun)
|
| R11 | 68 Ohm |  (blau-grün-schwarz-gold-braun) (blau-grün-schwarz-gold-braun)
|
| R13 | 1500 Ohm |  (braun-grün-schwarz-braun-braun) (braun-grün-schwarz-braun-braun)
|
USB Zenerdioden
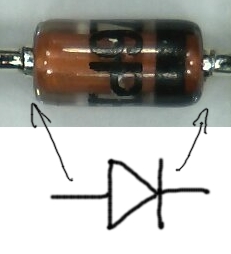
Nun benötigen wir zwei 3.6 V Zenerdioden für die Datenleitungen, Z1 und Z2. Hier muss auf die Orientierung geachtet werden. Die (schwarze) Linie auf den Dioden gehört auf die Seite der einzelnen Linie auf dem Diodensymbol (gegenüber des Dreiecks) das auf das PCB gedruckt ist. Dies ist auf dem Bild auf der linken Seite zu sehen.
Reset Resistor
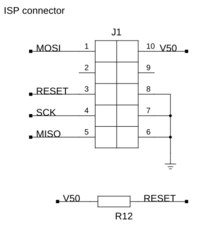
The Reset pin gets a 10 kOhm resistor R12 to the 5 V line. Again, have a look in the table for the correct color markings. Orientation is irrelevant.
| Name | Value | Color Code |
|---|---|---|
| R12 | 10 kOhm |  (brown-black-black-red-brown) (brown-black-black-red-brown)
|
Column Resistors
If you bought a kit or attend a workshop, you probably already got the correct Resistors. There should be (at least) nine of the same value. Just solder them into the places for R1 to R9.
If you are supplying your own LEDs or did not get matching resistors for any other reason, you have to pay attention: The ideal column resistors should be chosen for each LED color separately. You are always on the safe side, if you choose a high value, but then your cube may not be as bright as you want it to be. If you are interested in this, read LED Cube/Column Resistors in Detail. Alternatively, here is a table of common colors, their forward voltages and the recommended resistor value:
| Color | Forward Voltage | Resistor Value | Color Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red | 1.9 V | ? | Datei:R-?.jpeg (?-?-?-?-?) |
Column and Plane Connectors
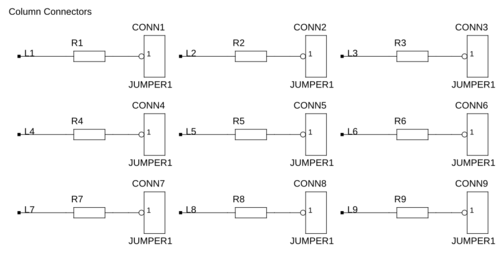
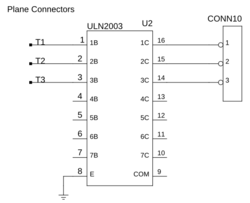
Now add the column and plane connectors to CONN1 to CONN10.
Capacitors
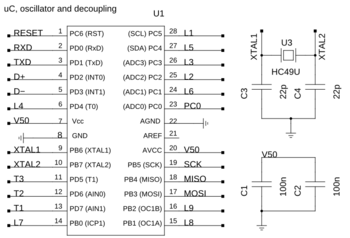
We need four capacitors, two times 100 nF (C1, C2) and two times 22 pF (C3, C4). See the schematic at the left or the table below for their values and positions. Again, all four devices are symmetric and orientation is irrelevant.
| Name | Value | Marking |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 100 nF | 104 |
| C2 | 100 nF | 104 |
| C3 | 22 pF | 220 |
| C4 | 22 pF | 220 |
Crystal
Now you should add the 16 MHz crystal U3. You do not have to care about its orientation.
-
16 MHz Crystal
Transistor Array
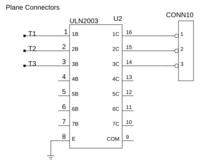
Now add the transistor array U2. Pay attention to the orientation! There is a marker in the package that can also be seen on the PCB.
Microcontroller socket

Add the microcontroller socket to the PCB at U1. As with the Transistor array, there is a small marker on the package which should be on the same side as the marker on the PCB.
USB Socket

Now add the USB socket. This should be straightforward. You should solder the two big shield connectors on the side, not just plug them in, to increase the stability.
Bootloader Jumper
Now we need the bootloader Jumper CONN12.
